In the realm of modern medicine, understanding a patient’s respiratory and metabolic health is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. This is where the ingenious invention of the arterial blood gas (ABG) kit comes into play. An ABG kit provides vital information about a patient’s blood oxygen levels, carbon dioxide levels, and blood pH, helping healthcare professionals make informed decisions about patient care.
What is an Arterial Blood Gas Kit?
An arterial blood gas (ABG) kit is a specialized medical device used to collect and analyze a sample of arterial blood. Unlike venous blood, which is drawn from veins, arterial blood is taken directly from an artery, providing a more accurate reflection of lung function and the body’s acid-base balance.
Importance of Arterial Blood Gas Analysis
ABG analysis provides critical insights into a patient’s respiratory and metabolic status. It helps assess conditions such as:
- Respiratory distress: Measuring oxygen and carbon dioxide levels to determine the effectiveness of breathing.
- Kidney failure: Evaluating the kidneys’ ability to regulate the body’s acid-base balance.
- Diabetic ketoacidosis: Monitoring blood pH levels to detect and manage this potentially life-threatening complication of diabetes.
- Drug overdose: Assessing respiratory function and acid-base balance in cases of overdose.
Components of an Arterial Blood Gas Kit
A standard ABG kit typically comprises the following components:
- ABG Syringe: A specialized syringe pre-heparinized to prevent blood clotting, ensuring accurate analysis.
- Needle: A small-gauge needle designed for arterial puncture.
- Antiseptic Wipe: Used to clean the puncture site and reduce infection risk.
- Gauze Pad: Applied to the puncture site after blood collection to stop bleeding.
- Bandage: Secures the gauze pad and protects the puncture site.
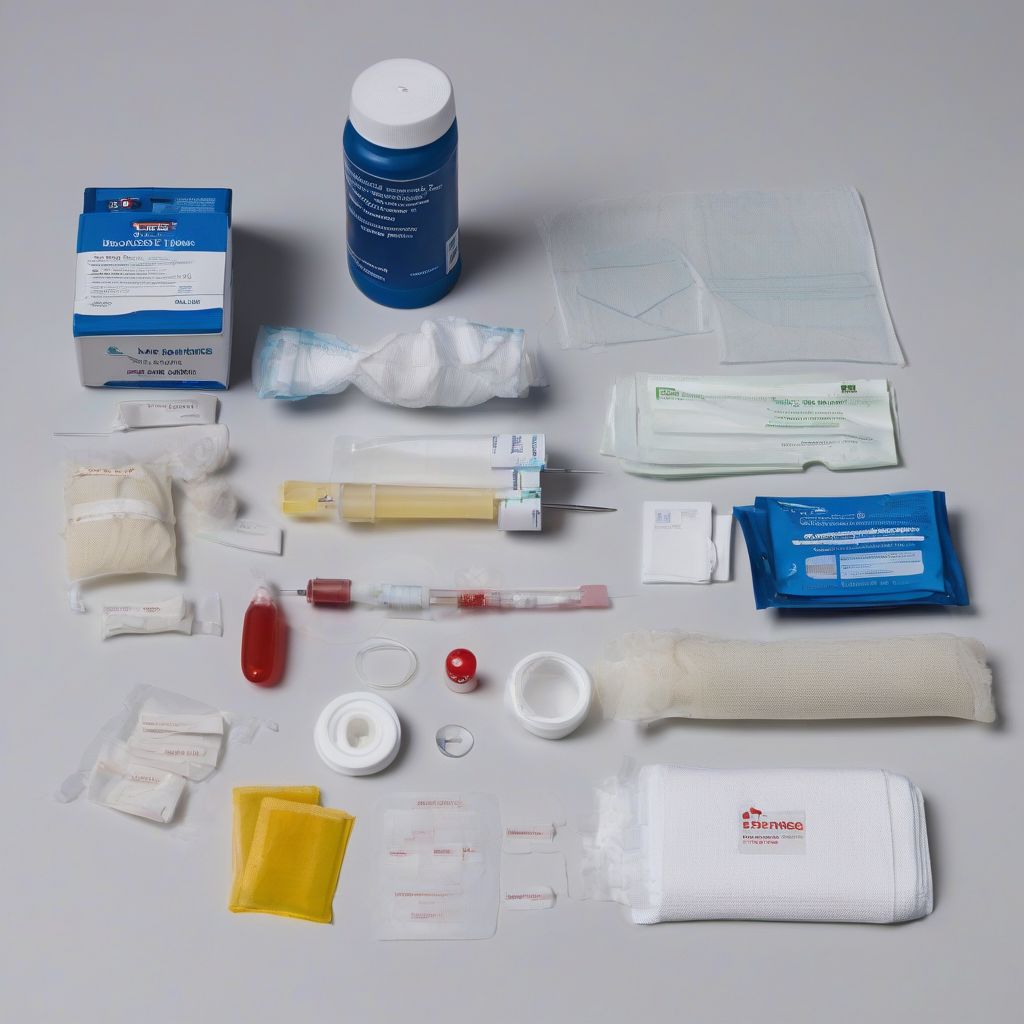 dulichchicago.com/arterial-blood-gas-kit/">Arterial Blood Gas Kit components" width="1024" height="1024">arterial blood gas kit components
dulichchicago.com/arterial-blood-gas-kit/">Arterial Blood Gas Kit components" width="1024" height="1024">arterial blood gas kit components
How is an Arterial Blood Gas Test Performed?
Collecting an arterial blood sample requires specialized training and should only be performed by qualified healthcare professionals. The process typically involves the following steps:
- Patient Preparation: The patient’s medical history and current medications are reviewed.
- Artery Selection: The radial artery in the wrist is commonly used, but other arteries may be chosen based on the patient’s condition.
- Site Preparation: The chosen puncture site is cleaned with an antiseptic wipe.
- Arterial Puncture: Using a sterile needle, the healthcare provider punctures the artery and collects a small blood sample.
- Sample Handling: The collected blood is immediately transferred to the ABG syringe, which is then placed in ice water for transport to the lab.
- Laboratory Analysis: The blood sample is analyzed using a specialized ABG analyzer to determine oxygen, carbon dioxide, and pH levels.
Interpretation of Arterial Blood Gas Results
Interpreting ABG results requires clinical expertise. Several parameters are considered, including:
- pH: Measures the acidity or alkalinity of the blood.
- PaO2: Partial pressure of oxygen, indicating the amount of oxygen dissolved in the blood.
- PaCO2: Partial pressure of carbon dioxide, reflecting the amount of carbon dioxide dissolved in the blood.
- HCO3-: Bicarbonate level, a measure of the body’s buffering system.
Based on these parameters, healthcare professionals can assess a patient’s respiratory and metabolic status and make informed decisions about treatment.
Importance of Accurate Arterial Blood Gas Analysis
Accurate ABG analysis is crucial for:
- Prompt Diagnosis: Identifying respiratory or metabolic imbalances early on.
- Treatment Monitoring: Evaluating the effectiveness of treatments, such as oxygen therapy or mechanical ventilation.
- Prognosis Prediction: Assessing the severity of illness and potential complications.
Advancements in Arterial Blood Gas Testing
Technological advancements have led to the development of portable ABG analyzers, allowing for rapid results at the point of care. These devices are particularly beneficial in critical care settings, where timely interventions can be life-saving.
Conclusion
Arterial blood gas analysis is a vital tool in modern medicine, providing crucial information about a patient’s respiratory and metabolic health. Understanding the components of an ABG kit, the procedure for collecting an arterial blood sample, and the interpretation of ABG results is essential for healthcare professionals involved in patient care. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more sophisticated and rapid ABG testing methods to emerge, further improving patient outcomes.